In a time when it appears almost every business around you is moving toward virtualization and/or the cloud, it is only natural to wonder whether you should make the move as well. Does it make sense for you to jump on the bandwagon or should you stick with your current tried and tested solution? While it is impossible to provide a blanket solution for all companies, knowing the facts will help you make an informed decision on what hosting solution will be best for your growing business. To revisit the basics, here are a few informative past articles:
Colocation Hosting
Dedicated Hosting
Cloud Hosting
Hybrid Hosting
Virtualization vs. Dedicated Servers
We often see that in most cases that solution doesn’t include putting all your apples into one basket. It is to go hybrid!
Last newsletter we discussed hybrid hosting in detail; its definition, the key benefits, and important factors to consider before choosing to go hybrid. To recap, hybrid cloud is one that mixes servers in the public cloud with other types of hosting such as collocated servers, leased dedicated servers, and/or private cloud servers. The public cloud has a number of advantages, but it doesn’t solve every hosting need. This is where hybrid comes in to mold the perfect solution. A company will use the public cloud to solve certain needs and then use other types of hosting that are a better fit for their more specific needs.
Here are a few example hybrid approach scenarios:
1. Public Cloud & Dedicated Environment
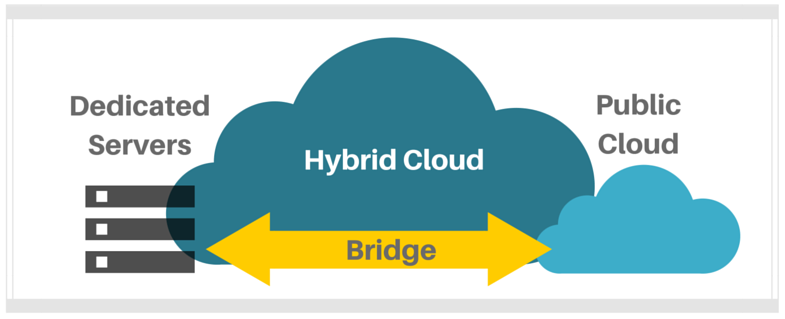
You have a web facing application that you are hosting entirely in a dedicated leased server environment. You are looking to cut costs by using a public cloud. However, your database processes large amounts of data and you are concerned that those workloads will not perform well in the cloud. A viable solution to this would be to offload your web application to the cloud and keep your database servers in the dedicated environment. This way you are saving costs where possible without compromising performance for your most data intensive workloads.
2. Public Cloud & Private Cloud
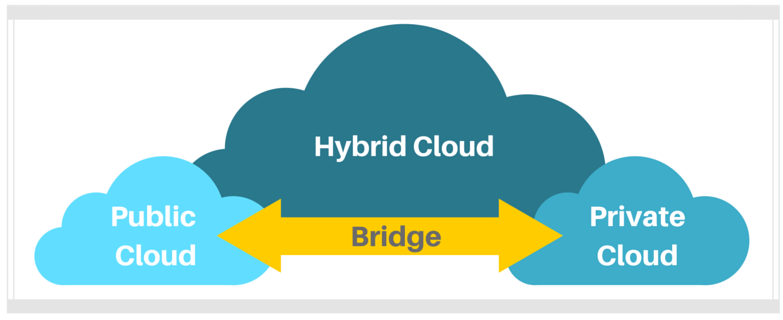
You own an ecommerce website where you sell a seasonal product, like swimsuits. Generally your site traffic is pretty steady except for the months of May and June leading into the summer, where you typically encounter large spikes. Your workloads in their steady state are handled in a fixed private cloud environment. But, you decide to offload these temporary traffic spikes to a public cloud, taking advantage of its on-demand scalable nature.
One other example hybrid approach is to add a dedicated cloud server within the public cloud infrastructure. This is a newer way to build a hybrid environment and takes full advantage of all the features of the public cloud while still having nearly full control of the dedicated environment. It is like having a private cloud but with the identical features and support of the public cloud. Since the dedicated server joins the public cloud infrastructure, you get a portal for self-management and scalability, just like with the public cloud. You have one cloud account for the public cloud and another for the dedicated cloud, but they look and work identically with all the same features. Additionally, you have access to all the networks in the public segment and the dedicated segment in both accounts so it is easy to add virtual servers. Lastly, there is no need for a cable drop since the two environments are already connected. This solution provides a lot of flexibility and scalability while also maintaining high control.
The key thing to consider when building a hybrid cloud environment is how to securely interconnect the different environments. Here are the two ways to connect the two separate networks:
- VPN connection between the two environments and
- Cloud Direct Connection
Most cloud providers should allow for a VPN connection. In the NetSource public cloud this is easy to setup. The advantages of this type of connection are that it is secure and little or no cost is added to your public cloud. The main disadvantage is performance since the network traffic traverses the Internet.
Most cloud providers also offer a Direct Connection feature between the public cloud and your other hosting infrastructure. These connections between different providers can get quite expensive, but the main advantage is performance since the data does NOT traverse the Internet – this is a direct and private cable connection. With NetSource, all you need to do is order the NetSource Cloud Direct Connect™ service and we will drop a cable that interfaces directly to your NetSource public cloud network.
There are numerous possibilities for implementing various solutions that take advantage of hybrid cloud environments. NetSource specializes in designing hybrid hosting solutions that fit each company’s individual needs. Contact NetSource today to find out how we can help you build, grow, or improve your hosting environment.
